Resilience Awareness
Resilience refers to the ability of individuals, communities, or systems to withstand, adapt to, and recover from adversity, shocks, or stressors (commonly referred to as disasters). The capacity of a system to resist, absorb, respond, adapt, and restore from the effects of climate change hazards in a timely and efficient manner is crucial for ensuring the well-being of urban environments especially in the face of climate change, rapid urbanization, urban intensification. Building resilience is commonly accomplished by preserving and restoring the system and its functions in the face of disasters/shocks. Resilience strategies are key in defining and prioritizing relevant climate change issues to guide effective responses. In the context of urban disaster resilience, three generalizable elements are identified: systems, agents, and institutions. Cultivating resilience is an ongoing process that involves developing and strengthening these elements over time, which enables individuals and communities to better cope with adversity and thrive in the face of uncertainties (i.e., disasters). Different qualities of disaster resilience encompass a range of attributes essential for building resilience within urban environments, including reflectiveness, robustness, redundancy, flexibility, resourcefulness, rapidity, inclusivity, and integration. To assess the resilience of a community/neighborhood/city, several indicators from socioeconomic, infrastructure, and institutional capabilities play a crucial role in describing the fundamental characteristics of the unit of analysis. These indicators assist decision-makers and planners in prioritizing different needs and actions to manage overall resilience more effectively.
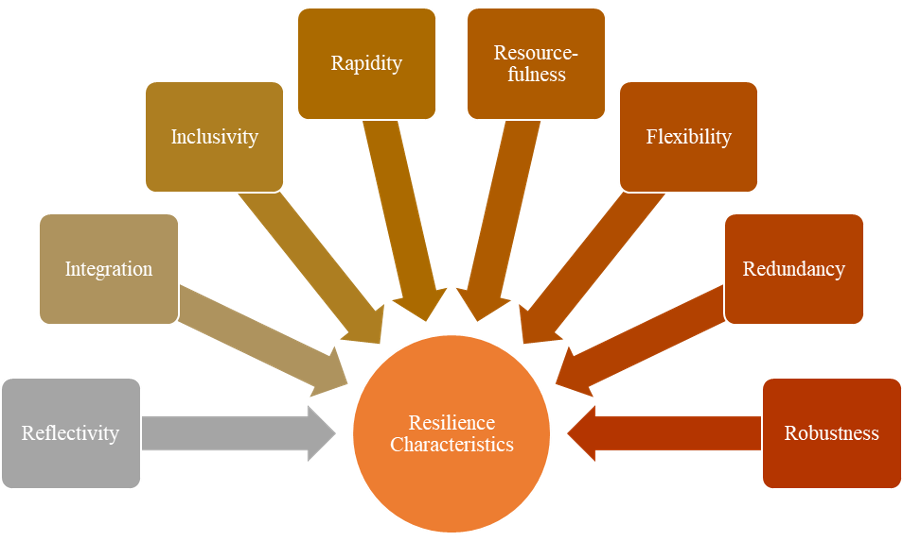
Resilience Characteristics