Overview
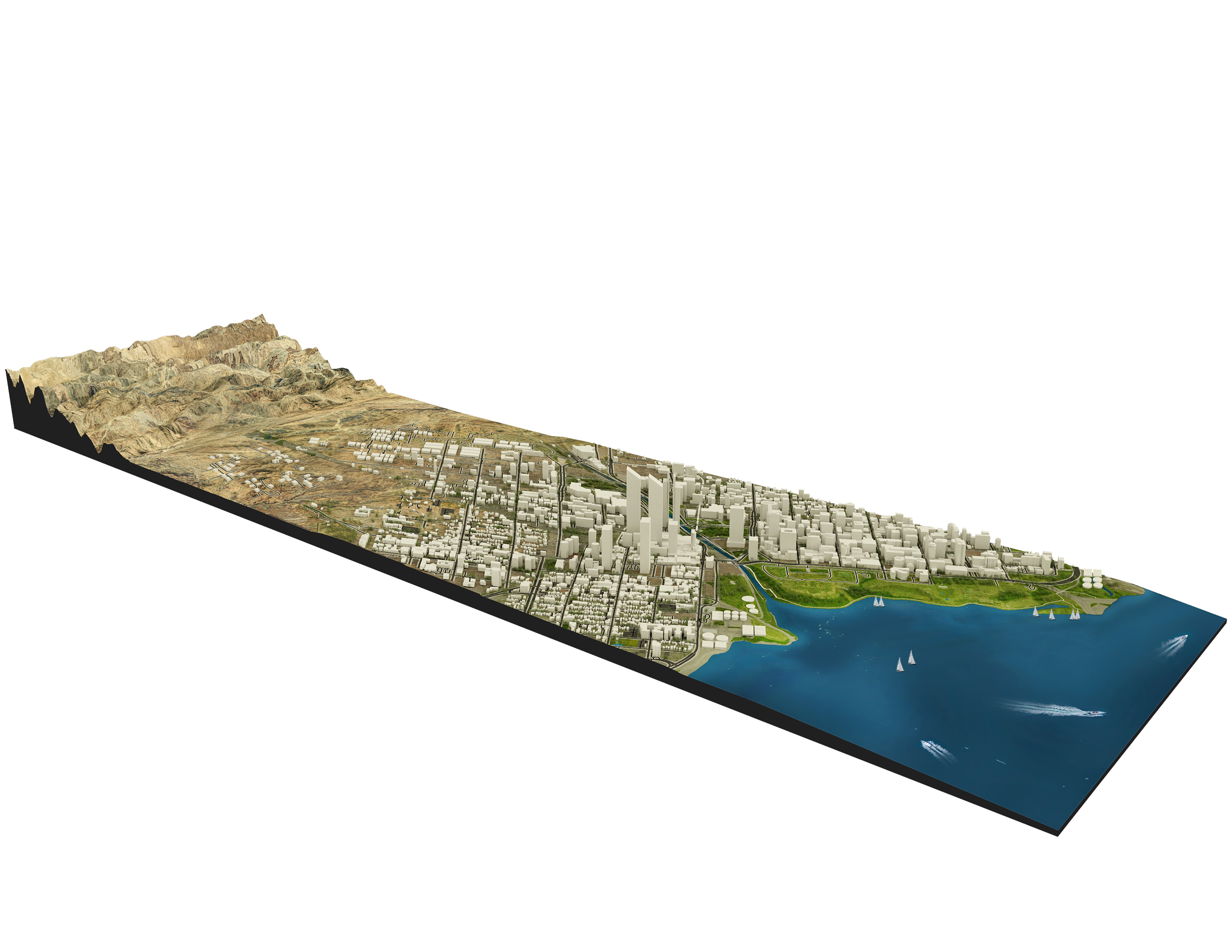
UrbanLab aims to design, research, and implement innovative solutions for urban development, emphasizing sustainability, eco-friendliness, and resilience. The lab envisions cities that harmonize human activities with the natural environment, ensuring a high quality of life for all inhabitants.
We collaborate with universities, government agencies, private companies, and non-profit organizations. These partnerships facilitate the exchange of knowledge, resources, and technologies to advance sustainable urban development.

Themes
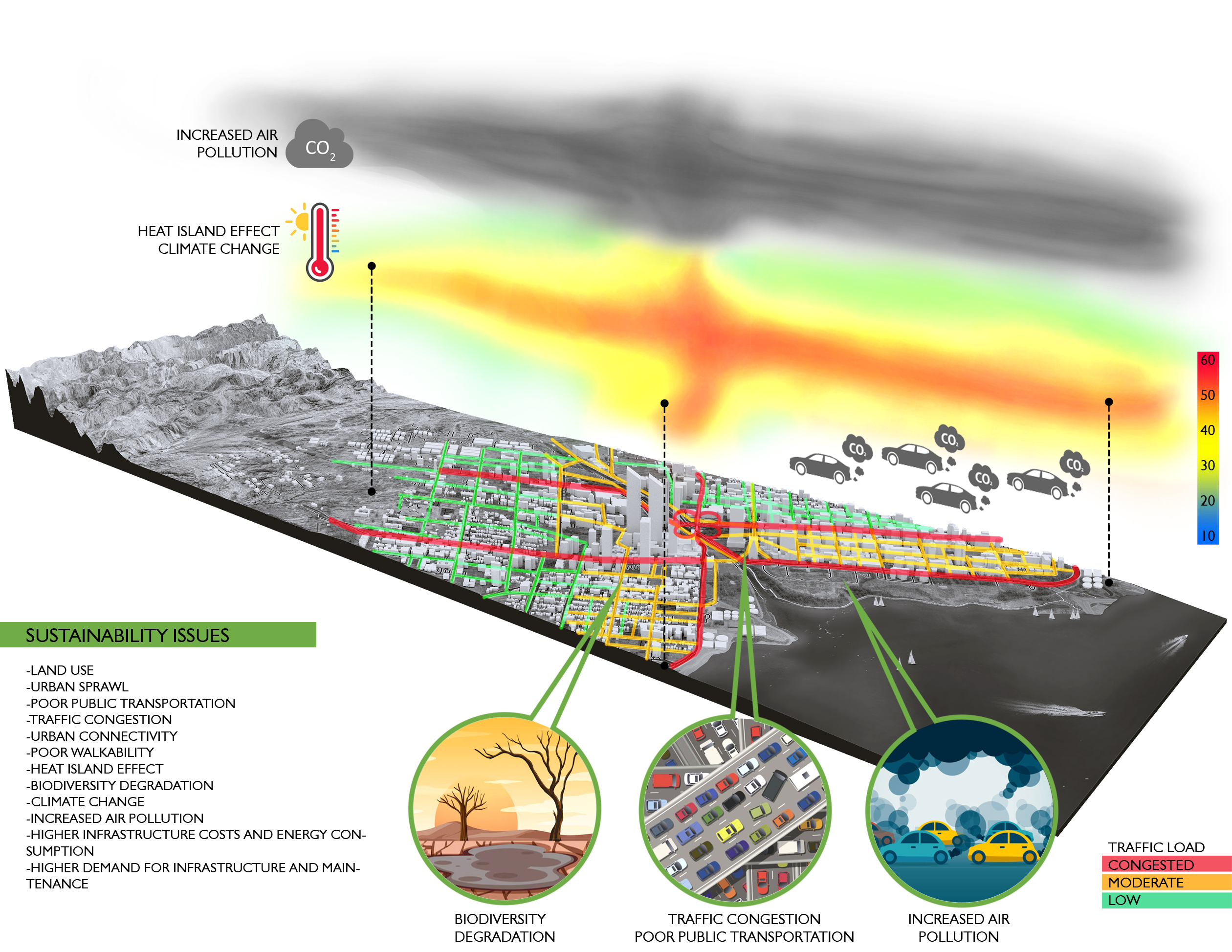
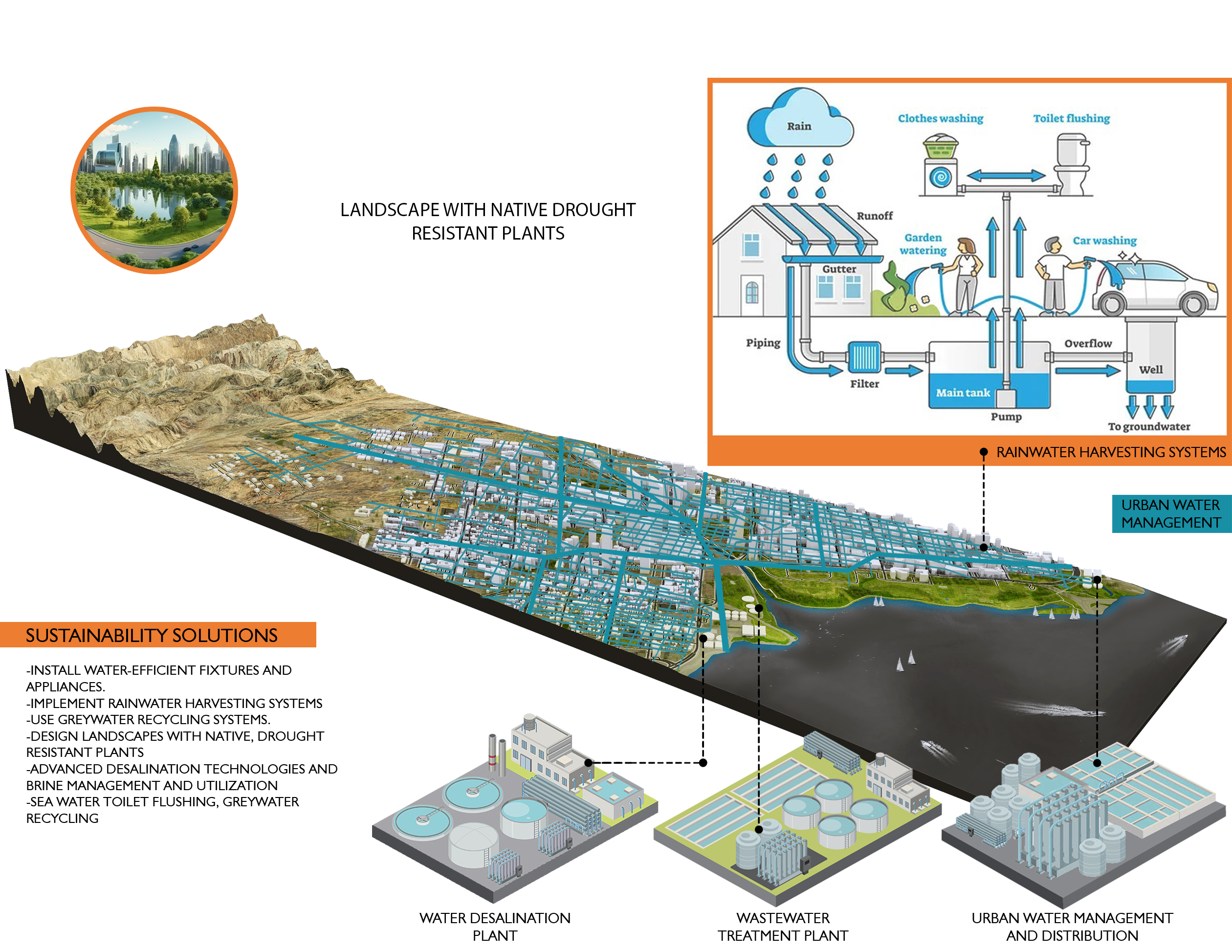
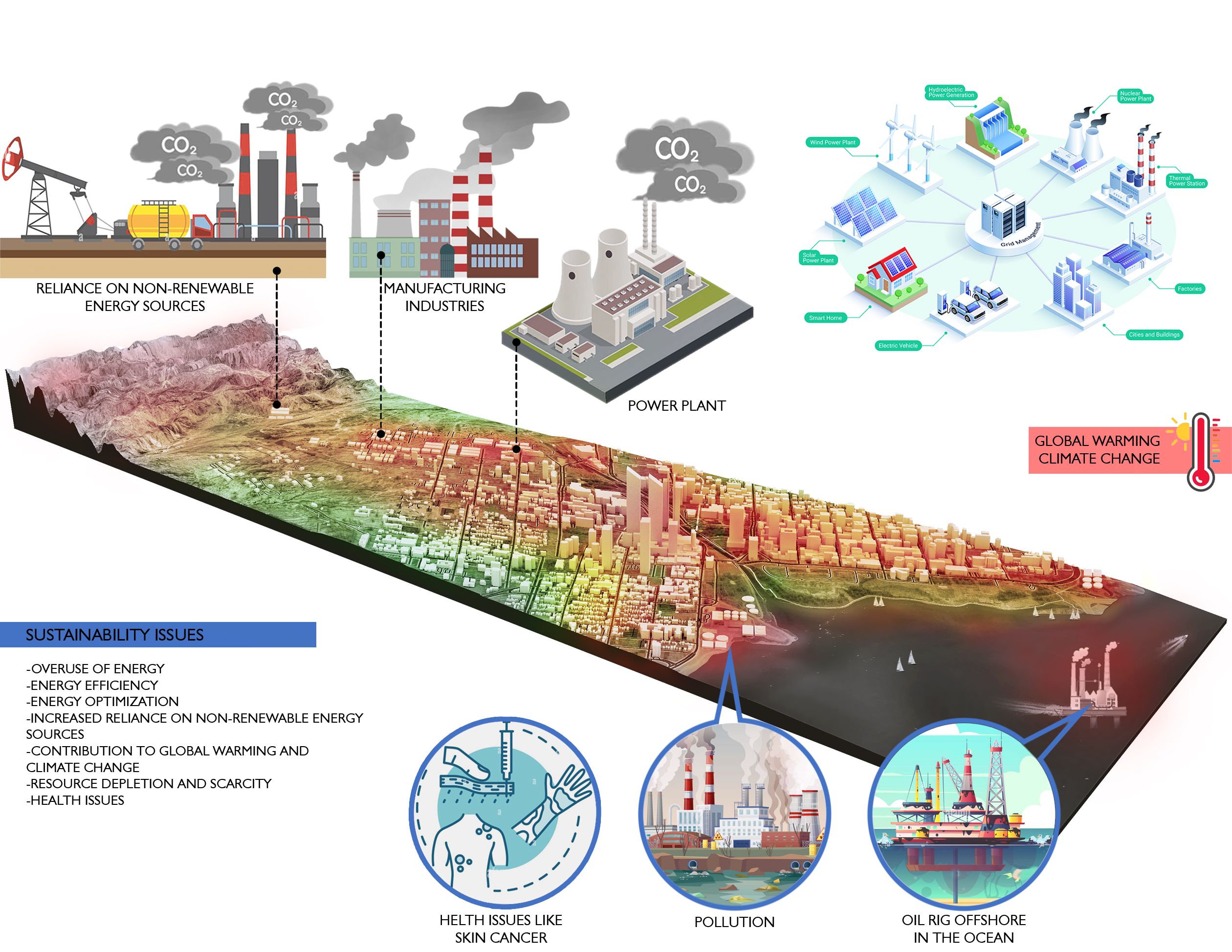
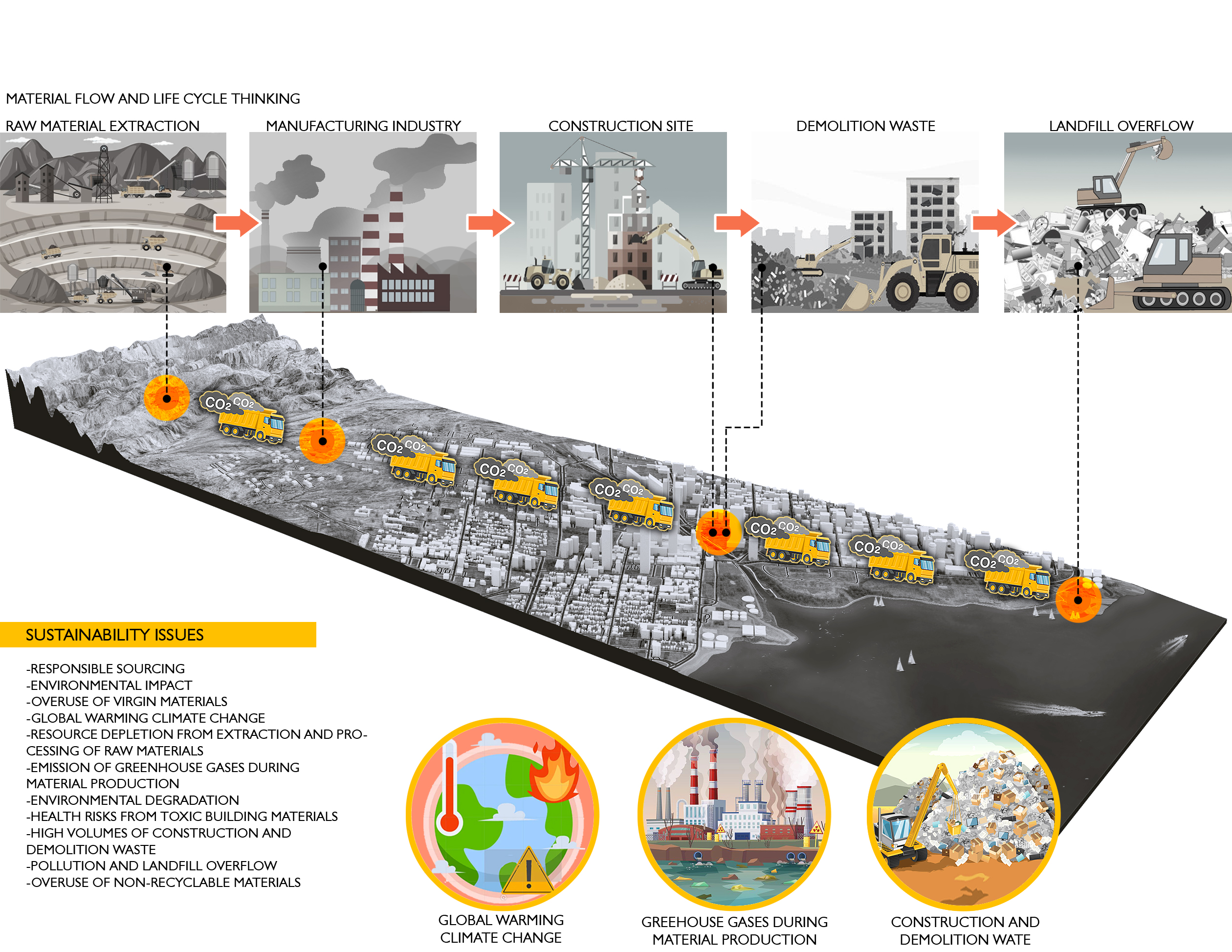
In the sustainability domain, we focus on developing and implementing practices that promote environmental stewardship and sustainable development. Our work includes comprehensive sustainability assessments, green building consulting, life cycle assessments, and environmental impact analyses.
- EXPLORE

Themes
Our resiliency theme centers on enhancing urbn areas' ability to withstand and adapt to climate change and other environmental challenges. We employ advanced risk assessment and adaptation strategies to help cities and businesses prepare for and respond to potential climate impacts.
- EXPLORE

Themes
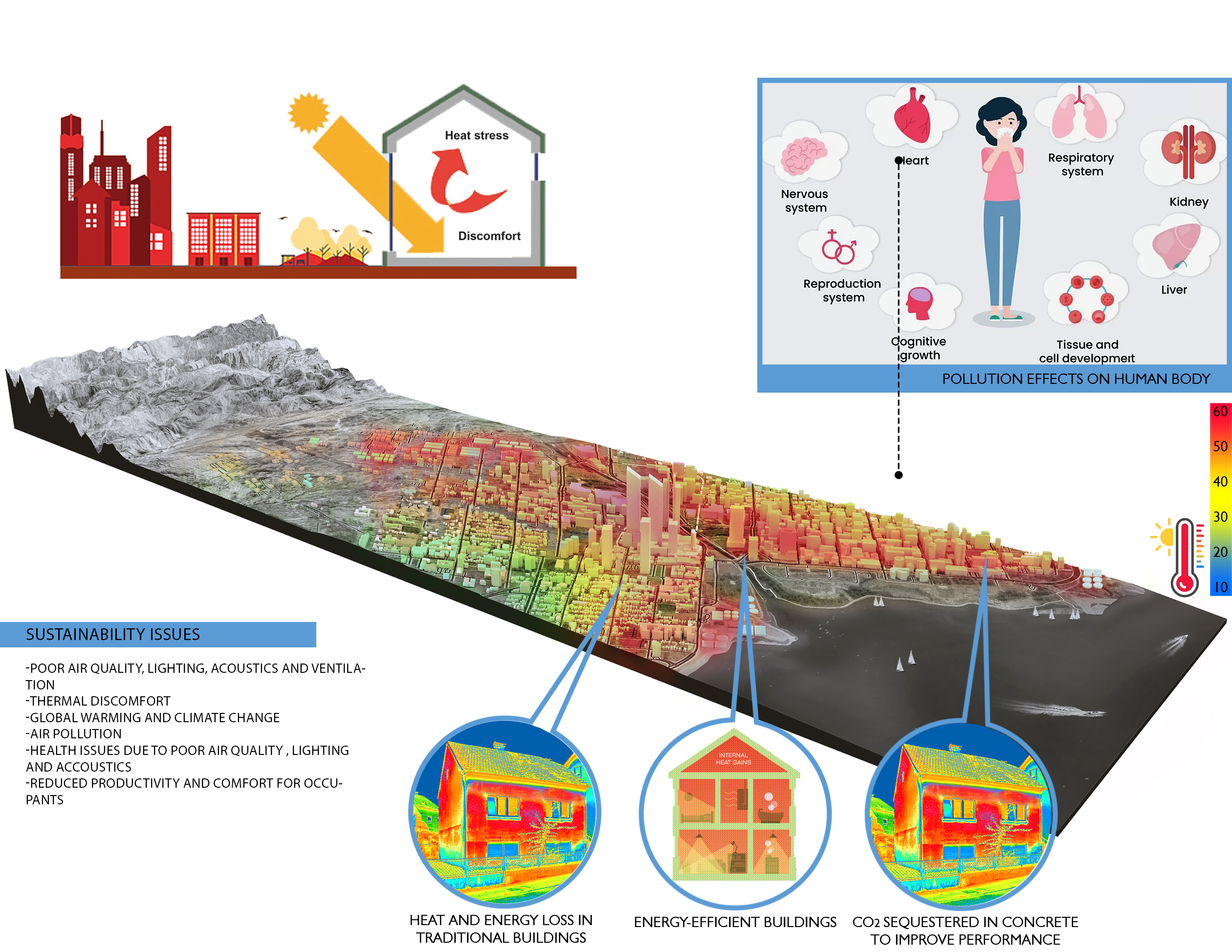
Livability emphasizes creating urban spaces that foster quality of life, health, and well-being for residents. Through innovative design, policy recommendations, and community engagement initiatives, we work to develop urban environments that are not only functional but also enriching and supportive for their inhabitants.